
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Parts of the сerebral cortex and the relative areas that are devoted to controlling various body regions
|
|
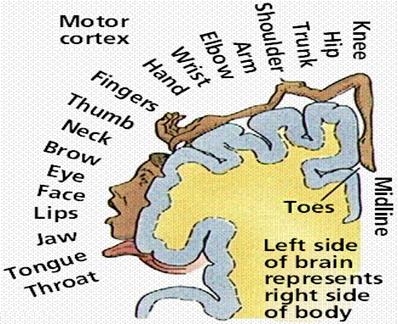 Fig.4
Fig.4
Spinal cord. The spinal cord runs along the dorsal side of the body and links the brain to the rest of the body. The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and dendrites. The surrounding white matter is made up of bundles of interneuronal axons (tracts). Some tracts are ascending (carrying messages to the brain), others are descending (carrying messages from the brain).
Senses. Input to the nervous system is in the form of our five senses: pain, vision, taste, smell, and hearing. Vision, taste, smell, and hearing input are the special senses. Pain, temperature, and pressure are known as somatic senses. Sensory input begins with sensors that react to stimuli in the form of energy that is transmitted into an action potential and sent to the CNS.
Sensory receptors. Sensory receptors are classified according to the type of energy they can detect and respond to:
· Mechanoreceptors: hearing and balance, stretching.
· Photoreceptors: light.
· Chemoreceptors: smell and taste mainly, as well as internal sensors in the digestive and circulatory systems.
· Thermoreceptors: changes in temperature.
· Electroreceptors: detect electrical currents in the surrounding environment.
Hearing. Hearing involves the actions of the external ear, eardrum, ossicles, and cochlea. In hearing, sound waves in air are converted into vibrations of a liquid then into movement of hair cells in the cochlea. Finally they are converted into action potentials in a sensory dendrite connected to the auditory nerve. Very loud sounds can cause violent vibrations in the membrane under hair cells, causing a shearing or permanent distortion to the cells, resulting in permanent hearing loss.
Photoreceptors detect vision and light sensitivity. The human eye can detect light in the 400-700 nanometer (nm) range, a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, the visible light spectrum. Light with wavelengths shorter than 400 nm is termed ultraviolet (UV) light. Light with wavelengths longer than 700 nm is termed infrared (IR) light.
Eye. In the eye two types of photoreceptor cells are clustered on the retina, or back portion of the eye. These receptors, rods and cones, apparently evolved from hair cells. Rods detect differences in light intensity; cones detect color. Rods are more common in a circular zone near the edge of the eye. Cones occur in the center (or fovea centralis) of the retina. Humans have three types of cones, each sensitive to a different color of light: red, blue and green.