Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
State the 1st law of Gossen. Give an appropriate example.
|
|
2-4
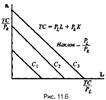 5) How does change isocost in response to changes in prices of factors of production? Given the differences in performance and prices of production factors, the fundamental challenge for manufacturers is to choose a combination of factors, which will provide the required output at minimum costs.Just as one and the same output can be produced by different combinations of factors, different combinations can give the same level of costs. Line, reflecting different combinations of factors of production, giving equal the total cost, is called izokostoy. Taking factor prices unchanged, and total costs - equal to the sum of fixed and variable costs TC = PKK + PLL, we can give a graphic description of izokost costs for different levels of C1, C2 and C3 (Figure 11.6).
5) How does change isocost in response to changes in prices of factors of production? Given the differences in performance and prices of production factors, the fundamental challenge for manufacturers is to choose a combination of factors, which will provide the required output at minimum costs.Just as one and the same output can be produced by different combinations of factors, different combinations can give the same level of costs. Line, reflecting different combinations of factors of production, giving equal the total cost, is called izokostoy. Taking factor prices unchanged, and total costs - equal to the sum of fixed and variable costs TC = PKK + PLL, we can give a graphic description of izokost costs for different levels of C1, C2 and C3 (Figure 11.6).
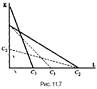
Each izokost describes all the possible combinations of factors that give the same level of total costs, while more highly placed izokosta reflects higher costs. Since each point izokosty reflects the same magnitude costs, the slope izokosty will be equal to the ratio of factor prices, taken with the opposite minus sign»: (-) PL / P.. If TC = PKK + PLL = const, then Δ KRK + Δ LPL = 0 or-Δ KRK = Δ LPL. Thus, Δ K / Δ L = PL / PK. The slope of the izokosty said that if the manufacturer replaces a unit of capital for labor, then to maintain the same level of costs, he can buy PL / PK units of capital at a price of pK or K = TC / RC - L (PL / PK). Naturally, in the case of price changes on one of the factors izokosty slope changes (Fig. 11.7). If we increase the price per unit of labor, izokosta become steeper (C1). Increasing the unit price of capital will flatter izokostu (C2). If you change the prices of both factors of production, the change in position izokosty (C3) will depend on changes in relative prices of factors PL / PK.
8.The Characteristics of Public Goods. To be called a public good, a good must exhibit two traits: there must be no way to exclude anyone from consuming it (nonexcludability), and one person’s consumption of the good must not diminish another person’s ability to consume the good (nonrivalry). Classic examples of public goods are lighthouses and the national defense. There are some problems that are associated with the providing of these particular goods, though.
21) Let the upper price ceiling is set above the equilibrium price. What are the implications of this decision of city authorities? They are surplus in the market.
22) Why in the long-term competitive firm makes zero economic profit? In thezero-profit equilibrium, the firm’s revenue must compensate the owners for the time and money that they expend to keep their business going.
23) Under establishing the upper ceiling prices could it be consumers which are the losers? If upper ceiling price is above equilibrium price then there will be deficit in the market. And consumers won’t have opportunity to buy necessary goods. But sometimes consumers would be the losers if it were market of labor and upper ceiling price would be below equilibrium price.
24) Why is the long-term competitive firm continues to produce, if it receives a zero economic profit? If the profit is positive, then other firms will enter in the market. And then profit will be less. If the profit is negative, firm will incur losses.
26) Formulate a definition of a market of perfect competition. Give examples of markets that are close to perfect competition.Under a perfectly competitive market structure is understood, in which buyers and sellers take prices as given, do not account for the response to the actions of other sellers, there are no barriers to entry. In such a market the number of sellers should be large enough, and none of them should not take up significant market share.
27) Give the definition of income elasticity of demand.
Income elasticity of demand is called the percentage change in quantity demanded per 1 percent change in income:
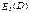 =
= 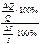 =
= 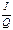 ×
× 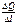 , where I is consumers income, Q is the quantity of demand. In the limit of infinitely small changes in income elasticity can be represented through the derivative
, where I is consumers income, Q is the quantity of demand. In the limit of infinitely small changes in income elasticity can be represented through the derivative
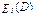 =
= 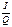
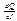 .
.
28) What market structure is called a monopoly?
Monopoly is a market structure in which a seller is a supplier of goods to the market, which has no close substitutes, while it may affect the price of their goods to enter the market closed, and the buyer accepts the price as given.
State the 1st law of Gossen. Give an appropriate example.
The function U (x, y) is called a utility function, if U (x ', y')> U (x ", y") if and only if the set of (x ', y') is preferable to set (x ", y ").
The task of selecting the user can be written as
max U (x, y) under 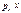 +
+ 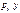 = I, x ≥ 0 y ≥ 0.
= I, x ≥ 0 y ≥ 0.
Marginal utility of goods is called an increase of the utility of consumption of an additional unit of that commodity. For goods X marginal utility is by definition equal 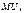 =
= 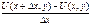 =
= 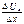 .
.
In the limit when ∆ x tends to zero, we obtain
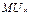 =
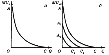
= 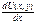 . Although the utility function U (x, y) is not uniquely defined, for it is a fair hypothesis that diminishing marginal utility: every unit of product increases the overall utility, but by a smaller amount than the previous one. Another name for this hypothesis - the first law of G. Gossen (1810-1858). This means that the marginal utility of goods decreases as its quantity.
. Although the utility function U (x, y) is not uniquely defined, for it is a fair hypothesis that diminishing marginal utility: every unit of product increases the overall utility, but by a smaller amount than the previous one. Another name for this hypothesis - the first law of G. Gossen (1810-1858). This means that the marginal utility of goods decreases as its quantity.
The first Gossen law (also law of the removing marginal utility) reads: " The size and the same benefit takes, if we continue continuously with preparing the benefit, continual off, to last saturation occurs.” The law means thus that the consumption of a property with increasing quantity donates a ever smaller auxiliary use (marginal utility).
Prime example is the consumption of food, with which typically saturation occurs (and in the consequence of the marginal utilities also negatively will can). Thus the benefit donates first glass of a water by one thirsty one a very high use, whereas second already brings a something more smaller and third again somewhat less additional use.