
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Muscles
|
|
Muscles and ligaments work together to control the movement of spine and support it during active and passive phase. There are three groups of lumbar spine muscles, divided according their function and position (Table 1). 1. Psoas major joins to the vertebrae bodies. It is flexor muscle of the hip joint. 2. Quadratus lumborum and the lateral intertransversarii behave as lateral flexors. They cover the transverse process anteriorly. 3. Intertransversarii mediales, interspinales, lumbar erector spinae, multifidi are extensor muscles. They support lumbar spine (Figure 4). (Hansen, Mark de Zee, 2006, 1888-1889.)
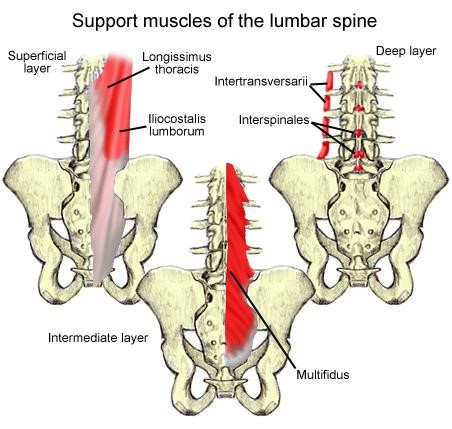
Figure 4. Muscles of the lumbar spine. (Website of MedScape, Lumbar Spine Anatomy, 2015)
Table 1. Lumbar spine muscles and their function by K. Bridwell (Website SpineUniverse).
| Muscles of the low back | Function |
| Psoas major | Flexes: hip joint flexion and vertebral column |
| Intertransversarii laterales | Lateral flexion of vertebral column |
| Quadratus lumborum | Lateral flexion of vertebral column |
| Intertransversarii mediales | Lateral flexion of vertebral column |
| Interspinales | Extends vertebral column |
| Multifidus | Extends and rotates vertebral column |
| Longissimus lumborum | Extends and rotates vertebral column |
| Iliocostalis lumborum | Extension, lateral flexion of vertebral column, rib rotation |
Moreover, the lumbar spine muscles can be classified by layers: deep and superficial. The deep layer muscle are intertansversarii medialis, interspinalis and multifidus. Multifidus muscle plays an important role in stabilization. Spinalis is a superficial muscle, which starts as a thick tendon from the sacrum up to the neck. Abdominal muscles are also important in stabilization of the back (Luomajoki, 2010, 13).