
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
http://themedicalbiochemistrypage.org/gene-regulation.php
|
|
The trp Operon
The trp operon (see diagram below) encodes the genes for the synthesis of tryptophan. This cluster of genes, like the lac operon, is regulated by a repressor that binds to the operator sequences. The activity of the trp repressor for binding the operator region is enhanced when it binds tryptophan; in this capacity, tryptophan is known as a corepressor. Since the activity of the trp repressor is enhanced in the presence of tryptophan, the rate of expression of the trp operon is graded in response to the level of tryptophan in the cell.
Expression of the trp operon is also regulated by attenuation. The attenuator region, which is composed of sequences found within the transcribed RNA, is involved in controlling transcription from the operon after RNA polymerase has initiated synthesis. The attenuator of sequences of the RNA are found near the 5' end of the RNA termed the leader region of the RNA. The leader sequences are located prior to the start of the coding region for the first gene of the operon (the trpE gene). The attenuator region contains codons for a small leader polypeptide, that contains tandem tryptophan codons. This region of the RNA is also capable of forming several different stable stem-loop structures.
Depending on the level of tryptophan in the cell and hence the level of charged trp-tRNAs, the position of ribosomes on the leader polypeptide and the rate at which they are translating allows different stem-loops to form. If tryptophan is abundant, the ribosome prevents stem-loop 1-2 from forming and thereby favors stem-loop 3-4. The latter is found near a region rich in uracil and acts as the transcriptional terminator loop as described in the RNA synthesis page. Consequently, RNA polymerase is dislodged from the template.
The operons coding for genes necessary for the synthesis of a number of other amino acids are also regulated by this attenuation mechanism. It should be clear, however, that this type of transcriptional regulation is not feasible for eukaryotic cells.
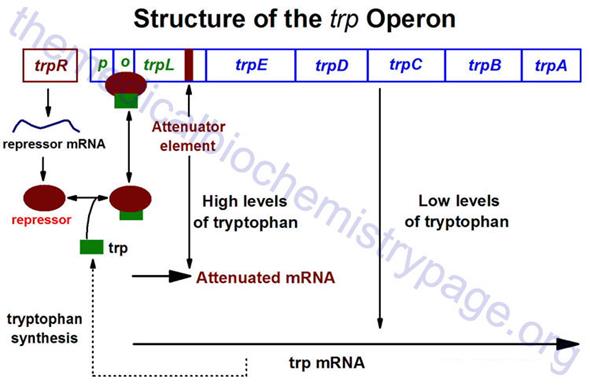
Regulation of the trp operon in E. coli. The trp operon is controlled by both a repressor protein binding to the operator region as well as by translation-induced transcriptional attenuation. The trp repressor binds the operator region of the trp operon only when bound to tryptophan. This makes tryptophan a co-repressor of the operon. The trpL gene encodes a non-functional leader peptide which contains several adjacent trp codons. The tructural genes of the operon responsible for tryptophan biosynthesis are trpE, D, C, B and A. When trptophan level are high some binds to the repressor which then binds to the operator region and inhibits transcription. The mechanism of attenuation of the trp operon is diagrammed below.
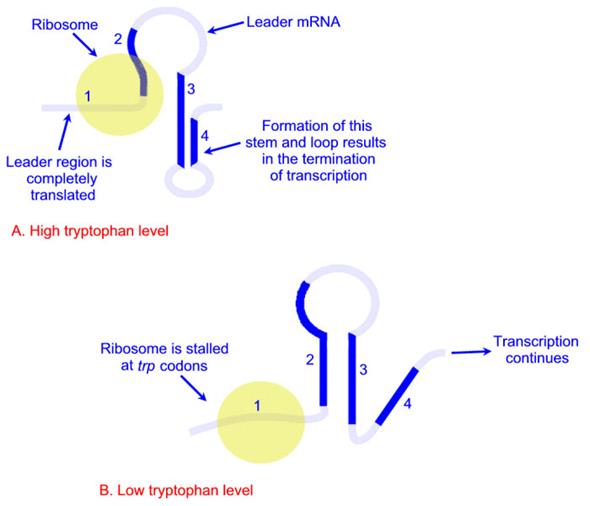
Attenuation of the trp operon. The attenuation region of the trp operon contains sequences that allow the resulting mRNA to form several different stem-loop structures. These regions are identified as 1 through 4. The stem-loops that are significant as to whether transcription is attenuated or not are formed between regions 2 and 3 or between regions 3 and 4. When tryptophan levels are high there is plenty of charged trp-tRNAs available and ribosomes translating the leader peptide encoded by the trpL gene do not stall at the repeated trp codons in the leader peptide. Under these conditions the ribosomes rapidly cover regions 1 and 2 of the mRNA which allows the stem-loop composed of regions 3 and 4 to form. The stem-loop formed by regions 3-4 results in a transcriptional termination structure and transcription of the trp operon ceases, i.e. is attenuated. Conversely, when tryptophan levels are low the level of charged trp-tRNAs will also be low. This leads to a stalling of the ribosomes within the leader peptide when they encounter the trp codon repeats. The ribosome stalls over region 1 of the mRNA which allows step-loop 2-3 to form and prevents the transcriptional termination stem-loop 3-4 from forming. The inability of this structure to form allows the entire operon to be transcribed and the tryptophan biosynthetic enzymes to be produced.
back to the top
|