
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
The indefinite article
⇐ ПредыдущаяСтр 4 из 4
|
|
COUNT AND NONCOUNT NOUNS
| 1. I bought a chair. Tom bought three chairs. 2. We bought some furniture. INCORRECT: We bought a furniture. INCORRECT: We bought some furnitures. | Chair is a count noun; chairs are items that can be counted. Furniture is a noncount noun. In grammar, furniture cannot be counted. | |||
| Singular Plural | ||||
| COUNT NOUN | a chair one chair | chairs two chairs some chairs a lot of chairs many chairs | A count noun: a) may be preceded by a/an in the singular; b) takes a final -s/-es in the plural. | |
| NONCOUNT NOUN | furniture some furniture a lot of furniture much furniture | ¾ | A noncount noun: a) is not immediately preceded by a/an; b) has no plural form; does not take a final -s/-es. | |
SOME COMMON NONCOUNT NOUNS
| 1. Whole groups made up of similar items: baggage, clothing, equipment, food, fruit, furniture, garbage, hardware, jewelry, junk, luggage, mail, machinery, make-up, money/cash/change, postage, scenery, traffic. |
| 2. Fluids: water, coffee, tea, milk, oil, soup, gasoline, blood, etc. 3. Solids: ice, bread, butter, cheese, meat, gold, iron, silver, glass, paper, wood, cotton, wool, etc. 4. Gases: steam, air, oxygen, nitrogen, smoke, smog, pollution, etc. 5. Particles: rice, chalk, corn, dirt, dust, flour, grass, hair, pepper, salt, sand, sugar, wheat, etc. |
| 6. Abstractions: — beauty, confidence, courage, education, enjoyment, fun, happiness, health, help, honesty, hospitality, importance, intelligence, justice, knowledge, laughter, luck, music, patience, peace, pride, progress, recreation, significance, sleep, truth, violence, wealth, etc. — advice, information, news, evidence, proof; — time, space, energy; — homework, work; — grammar, slang, vocabulary. 7. Languages: Arabic, Chinese, English, Spanish, etc. 8. Fields of study: economics, chemistry, engineering, history, literature, mathematics, psychology, etc. 9. Recreation: baseball, soccer, tennis, chess, bridge, poker, etc. 10. General activities: driving, studying, swimming, travelling, walking (and other gerunds). |
| 11. Natural Phenomena: weather, dew, fog, hail, heat, humidity, gravity, rain, lightning, sleet, snow, thunder, wind, darkness, light, sunshine, electricity, fire. |
USING NOUNS AS MODIFIERS
| 1. The soup has vegetables in it. It is vegetable soup. 2. The building has offices in it. It is an office building. | When a noun is used as a modifier, it is in its singular form. |
| 3. The test lasted two hours. It was a two-hour test. 4. Her son is five years old. She has a five-year-old son. | When a noun used as a modifier is combined with a number expression, the noun is singular and a hyphen (-) is used. |
THE INDEFINITE ARTICLE
| Use of a/an | Examples |
| 1. Before a singular countable noun, when it is mentioned for the first time and represents no particular person or thing: | I can see a book on the table. They live in a flat. He bought an ice-cream. |
| 2. Before a singular countable noun which is used as an example of a class of things: | A child needs love = All children need/Any child needs love. |
| 3. With a noun complement. This includes names of professions: | My friend is a manager. She'll be a dancer. |
4. With certain numbers.
Before half when half follows
a whole number.
But 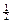 kg = half a kilo, though
a + half + noun is sometimes possible.
With kg = half a kilo, though
a + half + noun is sometimes possible.
With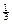 , , 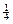 , etc a is usual: , etc a is usual:
| a dozen, a hundred, a million (but one dozen, one hundred, one million is also possible).
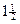 kilos = one and a half kilos or
a kilo and a half;
a half-holiday, a half-portion,
a half-share;
a third, a quarter etc., but one is also possible. kilos = one and a half kilos or
a kilo and a half;
a half-holiday, a half-portion,
a half-share;
a third, a quarter etc., but one is also possible.
|
| 5. In expressions of price, speed, ratio etc.: | 5p a kilo, sixty kilometres an hour, four times a day; (Here a/an=per) |
| 6. Before a singular countable noun after the word whatin exclamatory sentences and after the wordssuch, quite, rather: | Such a long queue! Such long queues! What a pretty girl! What pretty girls! She is still quite a child. It is rather a difficult problem. |
| 7. With the nouns in the function of apposition. But when the apposition refers to a well-known person the is used: | The report was made by Petrenko, a student of our University. Jack London, the great American novelist, was born in San Francisco. |
| 8. In a number of set expressions: a lot of, a great many, a great deal of, a good deal of, a great number of, a good many, a couple, a little, a few, at a speed of, at a time when, at a time, in time, on a large (small) scale, all of a sudden, by bus (train), to be in a hurry, to be in a position, to be at a loss, it’s a pity, for a short (long) time, as a result of, as a matter of fact, to have a good time, to have a mind, in a loud (low) voice, to have a look, to have a headache, to take a sit, to have a cold, to go for a walk. |