
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
The Commonwealth of Australia
|
|
Australia /ə ˈ streɪ ljə
/, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent as well as the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Australia is a country, an island, and a continent. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area. Neighbouring countries include Indonesia, East Timor and Papua New Guinea to the north; the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu and New Caledonia to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east.On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Since Federation, Australia has maintained a stable liberal democratic political system which functions as a federal parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy. The federation comprises six states and several territories. The population of 22.7 million is heavily concentrated in the Eastern states and is highly urbanised.
Australia is a constitutional monarchy with a federal division of powers. It uses a parliamentary system of government with Queen Elizabeth II at its apex as the Queen of Australia, a role that is distinct from her position as monarch of the other Commonwealth realms. The Queen resides in the United Kingdom, and she is represented by her viceroys in Australia (the Governor-General at the federal level and by the Governors at the state level), who by convention act on the advice of her ministers. Supreme executive authority is vested by the Constitution of Australia in the sovereign, but the power to exercise it is conferred by the Constitution specifically to the Governor-General. The most notable exercise of the Governor-General's reserve powers outside a Prime Minister's request was the dismissal of the Whitlam Government in the constitutional crisis of 1975.
The federal government is separated into three branches:
§ The legislature: the bicameral Parliament, defined in section 1 of the constitution as comprising the Queen (represented by the Governor-General), the Senate, and the House of Representatives;
§ The executive: the Federal Executive Council, in practice the Governor-General as advised by the Prime Minister and Ministers of State;
§ The judiciary: the High Court of Australia and other federal courts, whose judges are appointed by the Governor-General on advice of the Council.
The party with majority support in the House of Representatives forms the government and its leader becomes Prime Minister. In cases where no party has majority support, the Governor-General has the power to appoint the Prime Minister, and if necessary dismiss one that has lost the confidence of Parliament. Governor-General-Quentin Bryce, Prime Minister-Julia Gillard
There are two major political groups that usually form government, federally and in the states: the Australian Labor Party, and the Coalition which is a formal grouping of the Liberal Party and its minor partner, the National Party. Independent members and several minor parties—including the Greens and the Australian Democrats—have achieved representation in Australian parliaments, mostly in upper houses.
Australia has six states—New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia—and two major mainland territories—the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory (ACT).
Australia's landmass of 7, 617, 930 square kilometres (2, 941, 300 sq mi) is on the Indo-Australian Plate. Surrounded by the Indian and Pacific oceans, it is separated from Asia by the Arafura and Timor seas, with the Coral Sea lying off the Queensland coast, and theTasman Sea
lying between Australia and New Zealand. The world's smallest continent and sixth largest country by total area, Australia—owing to its size and isolation—is often dubbed the " island continent", and is sometimes considered the world's largest island.The Great Barrier Reef, the world's largest coral reef, lies a short distance off the north-east coast and extends for over 2, 000 kilometres (1, 240 mi). Mount Augustus, claimed to be the world's largest monolith, is located in Western Australia. At 2, 228 metres (7, 310 ft), Mount Kosciuszko on the Great Dividing Range is the highest mountain on the Australian mainland.
The Murray River (River Murray in South Australia) is Australia's longest river of 2, 995 kilometres (1, 861 mi) in length.
Although Australia has no official language, English is so entrenched that it has become the de facto national language. Australian English is a major variety of the language with a distinctive accent and lexicon. General Australian serves as the standard dialect. Spelling is similar to that of British English with a number of exceptions.
Canberra /ˈ kæ nbɛ rə
Sydney /sɪ dni
/ is the most populous city in Australia and the state capital of New South Wales. The city is built on hills surrounding Port Jackson which is commonly known as Sydney Harbour, where the iconic Sydney Opera House and the Harbour Bridge feature prominently. The hinterland of the metropolitan area is surrounded by national parks, and the coastal regions feature many bays, rivers, inlets and beaches including the famous Bondi Beach. Within the city are many notable parks, including Hyde Park and the Royal Botanic Gardens. Sydney ranks among the top 10 world centres.Other main cities are: Brisbane, Adelaide, Hobart, Melbourne, and Perth.
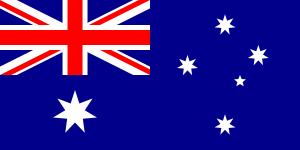
The Australian flag uses three prominent symbols: the Union Flag, the Commonwealth Star (also the Federation Star) and the Southern Cross. It is a defaced Blue Ensign: a blue field with the Union Flag in the canton (upper hoist quarter), and a large white seven-pointed star known as the Commonwealth Star in the lower hoist quarter. The fly contains a representation of the Southern Cross constellation, made up of five white stars – one small five-pointed star and four, larger, seven-pointed stars.