
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Text D. Sludge treatment and disposal
|
|
Sludge is the residue that accumulates in the STP. It is solid matter that has settled out of suspension in sewage undergoing sedimentation in tanks or basins. Since a considerable quantity of sludge is produced during the sewage treatment process, treatment and disposal of sewage sludge are major factors in the design and operation of all water pollution control plants. Two basic goals of sludge treatment before final disposal are:
· the reduction of sludge volume, which, in turn, reduces the costs of pumping and storage;
· the stabilization of the organic materials (stabilized sludge does not have an offensive odour and can be handled without causing a nuisance or health hazard).
Treatment methods of sewage sludge may include a combination of the following processes:
· thickening,
· digestion,
· dewatering,
· disposal.
Thickening is usually the first step in sludge treatment, because it is impractical to handle thin sludge, slurry of solids suspended in water. Thickening is usually accomplished in a tank called a gravity thickener. An alternative to gravity thickening is dissolved-air flotation.
Digestion is a biological process in which organic solids are decomposed into stable substances. Digestion reduces the total mass of solids, destroys pathogens, and makes it easier to dewater or dry the sludge. Most large STPs use a digestion system in which organics are metabolized by bacteria anaerobically (in the absence of oxygen), and in some STPs sludge digestion takes place aerobically (in the presence of oxygen). Both aerobic and anaerobic digestion converts about half of the organic sludge solids to liquids and gases.
Dewatering is dehydration, or water removal. Digested sewage sludge is usually dewatered before disposal. Dewatered sludge still contains a significant amount of water (about 70%), but even at that moisture content, sludge no longer behaves as a liquid and can be handled as a solid material. Sludge drying beds provide the simplest method of dewatering. Drying is a combination of evaporation and gravity drainage through the sand. After about six weeks of drying, the sludge cake may have a solids content of about 40%. Alternatives to sludge drying beds include the rotary-drum vacuum filter and the centrifuge.
Disposal. The final destination of treated sewage sludge usually is the land. Dewatered sludge can be:
· buried underground in a sanitary landfill;
· spread on agricultural land as a soil conditioner and fertilizer;
· incinerated if a suitable site for land disposal is not available, as in urban areas (in the case of incineration, air pollution control is a very important factor);
· dumped in the ocean (once an economical disposal method for many coastal communities, it is no longer considered a viable option);
· reutilized as an energy resource in many advanced countries.
***(an)aerobic digestion – (ан)аэробное сбраживание [перегнивание]
cake – кек, осадок на фильтре (слой твёрдых частиц, остающийся на фильтрующей поверхности после фильтрации суспензий)
gravity drainage – самотёчный дренаж
gravity thickener – гравитационный сгуститель
gravity thickening – гравитационное сгущение
land disposal – захоронение (отходов) в землю
offensive odour – отвратительный, неприятный, противный запах
rotary-drum – ротационно-барабанный
sanitary landfill – организованная свалка (обустроенная с учётом санитарных норм)
sewage sludge – осадок сточных вод
sludge drying bed – иловая площадка
sludge thickener – илоуплотнитель, сгуститель осадка
soil conditioner – почвоулучшитель
thin – жидкий; водянистый, разбавленный
water pollution control – борьба с загрязнением воды
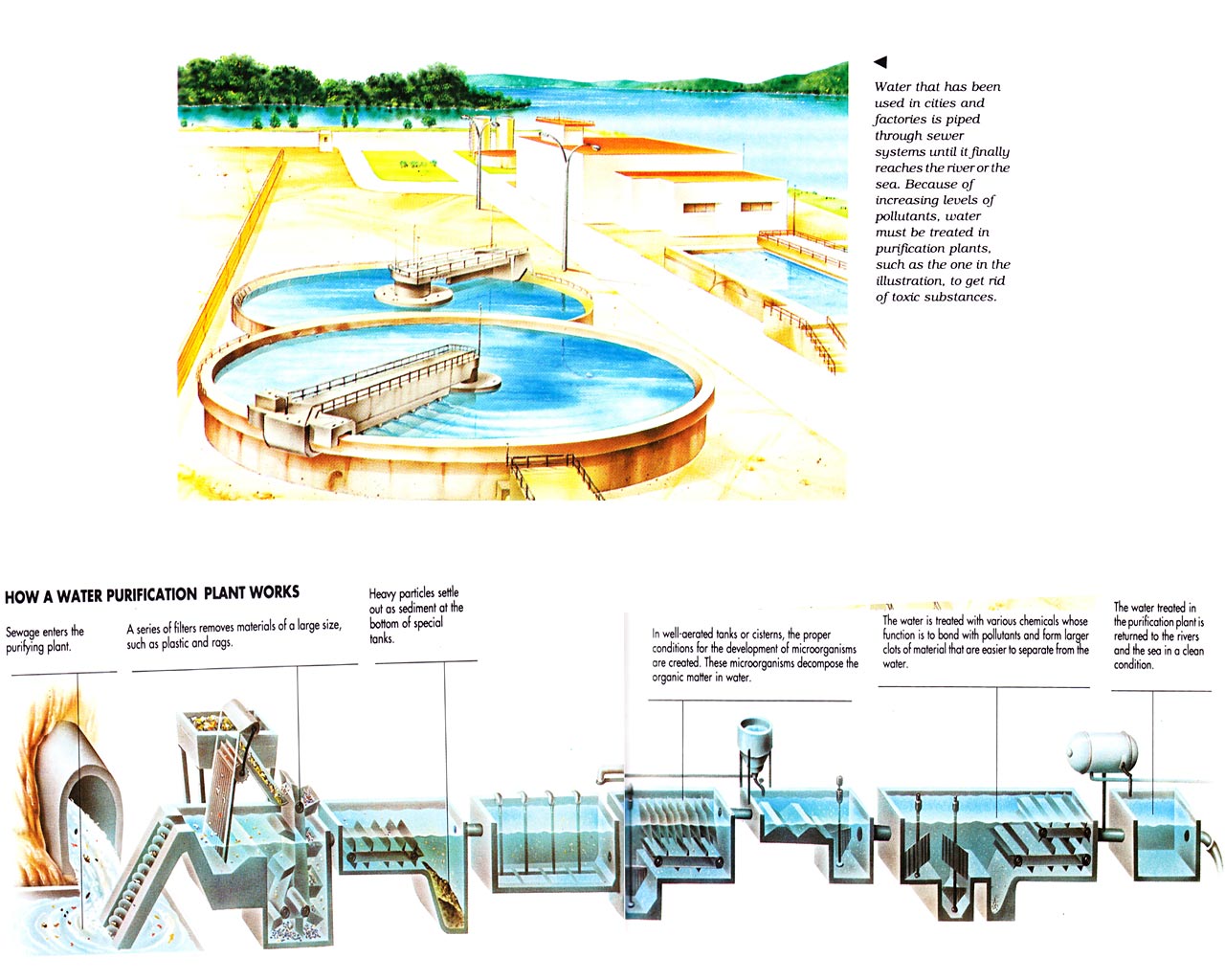
Pict. 3. How a water purification plant works