
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
International political and legal environment
|
|
45. Define and describe the international political environment. Name its key elements. How should the international managers deal with the foreign political environments?
The International Political Environment
Politics: the process of determining the distribution of power (the ability to control) within society.
International Politics: Bilateral political relations between home and host countries and the multilateral international policies governing the relations among groups of countries.
Who are Political Actors:
government members
political parties (including illegal parties)
public interest groups that are trying to affect the political
Supra-governmental entities (e.g. WTO, NAFTA)
Other corporations that might act in a political way
An international business faces a more complex task: It must obey the laws not only of its home country but also of all the host countries in which it operates. These laws determine the markets the.rms serve, the cost of goods and/or services they offer, the price they charge, and costs for labor, raw materials, and technology.
To understanding the politics and laws of both home and host countries, the international manager must consider the overall international political and legal environment.
o International law plays an important role in the conduct of international business. Although there is no body to enforce international law, certain treaties and agreements are respected by a number of countries and in.uence international business operations. The World Trade Organization (WTO) is such an international agency that de.nes internationally acceptable economic practices for its member countries. There are many other agreements that provide some legal regulation of international commerce, including the EU, North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and others. Similarly, the United Nations (UN) and its many allied organizations (such as the International Labor Organization, World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund) provide the legal and regulatory context within which global business operates;
o An important aspect of the political environment is the phenomenon of ethnicity —a driving force behind political instability around the world. Often, religious disputes lie at the heart of these differences. Many terrorist activities are also based on religious differences, as in the Middle East. Managers must understand the ethnic and religious composition of the host country in order to anticipate problems of general instability as well as those of an operational nature—such as effects on your workforce, on production and access to raw materials, and your market. For examplre: In Cyprus, it is important to understand the differences and similarities between the Greek and Turkish Cypriots; In Malaysia it is essential to recognize the special economic relationship between Chinese and Malay;
o Managers must be aware of the legal systems in the countries in which they operate and the legal relationship that exists between countries and the degree of independence of the judiciary from the political process
Common law is based on tradition, precedent, and custom and usage. The courts ful.ll an important role by interpreting the law according to these characteristics. UK and USA
A civil law system, also called a codi.ed legal system, is based on a detailed set of laws organized into a legal code. Over 70 countries, including Germany, France, and Japan operate on a civil law basis
One important difference between common law and civil law systems is apparent in the roles of judges and lawyers. In a common law system the judge serves as a neutral referee, ruling on various motions by the opposing parties’ lawyers. These lawyers are responsible for developing their clients’cases and choosing which evidence to submit on their clients’ behalf.
An example of an area in which the two systems differ in practice is contracts. In a common law country, contacts tend to be detailed, with all contingencies spelled out. In a civil law country, contracts tend to be shorter and less speci.c because many of the issues that a common law contract would cover are already included in the civil code. Thus, when entering into contracts abroad, it is important for the manager to understand which type of legal system will establish the contract.
Theocratic Law is based on the of.cially established rules governing the faith and
practice of a particular religion. In Iran, for example, a group of mullahs, or holy men, determine the legality or illegality through their interpretation of the Koran, the holy book of Islam. Muslim businesses often rely on leasing arrangements, rather than borrowing money, to obtain long-term assets.
o Countries often impose protectionist policies, such as tariffs, quotas, and other trade restrictions, to give preference to their own products and industries. The American auto industry continues to ask the US government for protection from Japanese car imports.
A country’s tax system in.uences the attractiveness of investing in that country and affects the relative level of pro.tability for an MNC.
The level of government involvement in the economic and regulatory environment varies a
great deal among countries and has a varying impact on management practices. In Canada, the government has a signi.cant involvement in the economy.
Managers should prepare themselves accordingly with an analysis of interest rates and stock prices, the country’s balance of payments, projections of probable macroeconomic policies, and.scal and current account de.cits.
46. What is political risk? What are the sources of political risk for international companies? How are they connected with the types of political risks?
- Political actions that affect business
Direct Effect -- The chance that political actors will change laws, regulations, etc. or take other actions that directly affect business;
Indirect Effect -- The chance that political actors will change the economic environment, the attitudes of the population, or some other contextual factor that then indirectly affects specific businesses.
Political risk deals with: political structure(the governance system of a country);
authority (nature of particular governors); legitimacy (the response of the population
to the government); culture (the nature of the society being governed)
Sources:
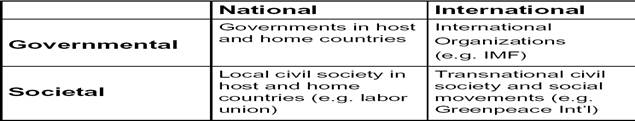
Types:
-Governmental (Formal and informal political parties and government officials)
- Societal (NGOs, public interest groups, strong individual actors, local companies)
- External (stemming from the international environment): Supranational agencies, foreign governments and NGOs