
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Descriptions and functions of some important organs of speech
|
|
PHONETICS
There are 26 letters in English and 44 speech sounds which are usually called phonemes. The phoneme is the smallest distinctive unit of language. e.g. bitter –butter-batter-better, these four words are distinguished from one another by the vowel sounds {I, A, ж e}.
An actually pronounced speech sound is always a variant of a phoneme, as it is always influenced by other neighboring phonemes; this variant is called an allophone. Thus, sounds {t} in the words “tree”, “ten”, “twenty” and “eighth” are allophones of the phonemes {t}, as in each case the pronunciation of this sound is slightly different.
ORGANS OF SPEECH
The organs, which take part in the production of speech sounds, are called speech
organs. When we speak, air comes out through the lungs and it is interfered at
various places for the production of sounds. Sounds cannot be produced without air.
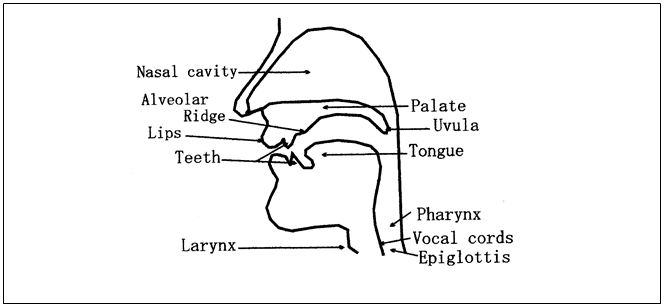
The following diagram shows the main organs of speech.
Important organs
Lips 5. Larynx 9. Soft palate
Teech 6. Vocal cords 10. Uvula
Alveolar ridge 7. Epiglottis 11. Hard palate
Tongue 8. Pharynx
Descriptions and functions of some important organs of speech
Þ The vocal cords
The larynx contains two small bands of elastic tissues. They are called vocal cords. The main function of the vocal cords is to produce voiced and voiceless sounds. The opening between the vocal cords is called epiglottis. When we breath in or out, the glottis is open. This is the position of the production of voiceless sounds like /p/, /t/, /k/, etc are voiceless sounds in English. The sounds when the glottis comes together are called voiced sounds like /b/, /d/, /g/.
Þ The soft palate
The soft palate is the roof of the mouth. It separates the oral and nasal cavity. The last part of the
soft palate is called uvula. When it is lowered, the nasal sounds (etc.m, n, ŋ) are produced.
When it is raised, the air passes out through the oral cavity and the oral sounds (etc.p, t, k, s) are
produced.
Þ The tongue
The tongue is an important organ of speech. It has the greatest variety of movement. It is divided
into four parts: the tip, the blade, the front and the back. The number of vowels is produced with the
help of the tongue. Vowels differ from each other because of the position of the tongue.
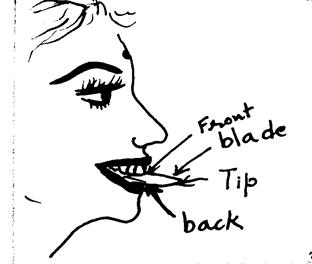 Picture of the tongue
Picture of the tongue
The tip of the tongue helps to produce /t, d, z, etc/. The blade of the tongue helps to produce /t∫, dÎ, ∫, etc/. The front of the tongue helps to produce palatal sound /j/ and the back of the tongue helps to produce /k, g/ sounds.