
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Introduction. Australia's national flag comprises
|
|
Australia
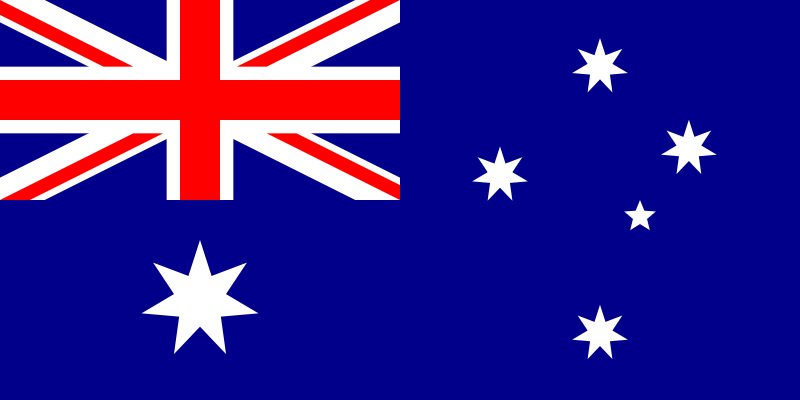

Australia's national flag comprises
the Union Jack, the Commonwealth Star, and the Southern Cross.

Australian Coat of Arms
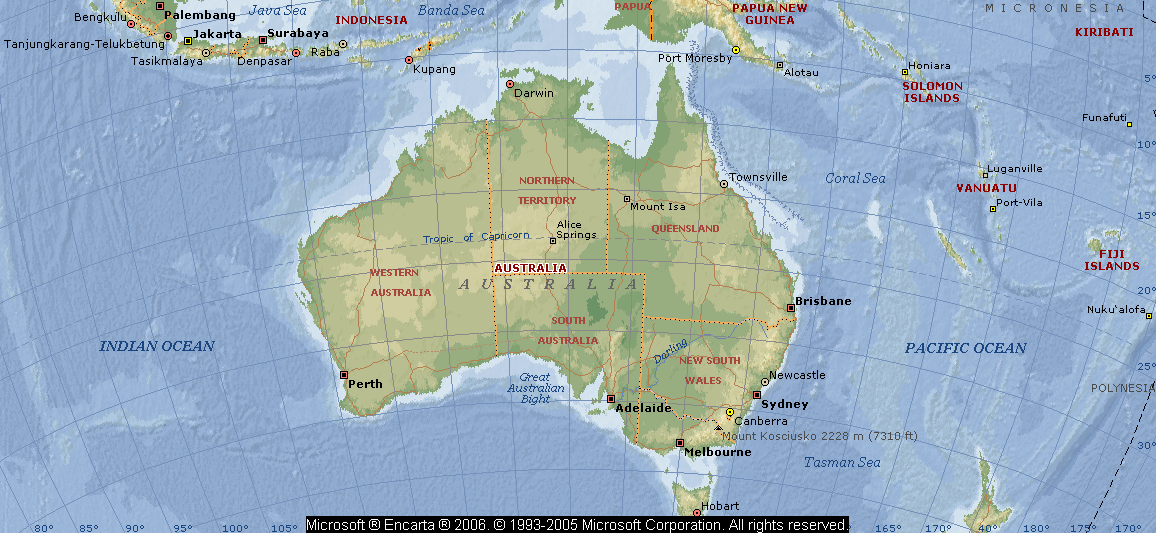
 States and Territories
States and Territories

Port Arthur, Tasmania was Australia's largest gaol for transported convicts
Introduction
Australia, the smallest continent, between the Indian and Pacific oceans. With the island state of Tasmania to the south, the continent makes up the Commonwealth of Australia, a federal parliamentary state (2005 est. pop. 20, 090, 000), 2, 967, 877 sq mi (7, 686, 810 sq km). Australia's capital is Canberra. Its largest city is Sydney, closely followed in population by Melbourne. There are five continental states (Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, and Western Australia, in addition to the aforementioned Tasmania) as well as the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory (an enclave within New South Wales, containing Canberra). Australia's external territories include Norfolk Island, Christmas Island, the Cocos (Keeling) Islands, and the Australian Antarctic Territory.
Land

The Australian continent extends from east to west some 2, 400 mi (3, 860 km) and from north to south nearly 2, 000 mi (3, 220 km). It is on the whole exceedingly flat and dry. Less than 20 in. (50.8 cm) of precipitation falls annually over 70% of the land area. From the narrow coastal plain in the west the land rises abruptly in what, from the sea, appear to be mountain ranges but are actually the escarpments of a rough plateau that occupies the western half of the continent. It is generally from 1, 000 to 2, 000 ft (305–610 m) high but several mountain ranges rise to nearly 5, 000 ft (1, 520 m); there are no permanent rivers or lakes in the region. In the southwest corner of the continent there is a small moist and fertile area, but the rest of Western Australia is arid, with large desert areas.
The northern region fronts partly on the Timor Sea, separating Australia from Indonesia; it also belongs to the plateau, with tropical temperatures and a winter dry season. Its northernmost section, Arnhem Land (much of which is an aboriginal reserve), faces the Arafura Sea in the north and the huge Gulf of Carpentaria on the east. On the eastern side of the gulf is the Cape York Peninsula, which is largely covered by woodland. Off the coast of NE Queensland is the Great Barrier Reef, the world's largest coral reef.
In E Australia are the mountains of the Eastern Highlands (a system of mountain ranges and plateaus in eastern Australia, also known as the Great Divide or Great Dividing Range), which run down the entire east and southeast coasts. The rivers on the eastern and southeastern slopes run to the Coral Sea and the Tasman Sea through narrow but rich coastal plains; the rivers on the western slopes flow either N to the Gulf of Carpentaria or W and SW to the Indian Ocean. The longest of all Australian river systems, the Murray River and its tributaries, drains the southern part of the interior basin that lies between the mountains and the great plateau. The rivers of this area are used extensively for irrigation and hydroelectric power.
Australia, remote from any other continent, has many distinctive forms of plant life—notably species of giant eucalyptus—and of animal life, including the kangaroo, the koala, the flying opossum, the wallaby, the wombat, the platypus, and the spiny anteater; it also has many unusual birds. Foreign animals, when introduced, have frequently done well. Rabbits, brought over in 1788, have done entirely too well, multiplying until by the middle of the 19th cent. they became a distinct menace to sheep raising. In 1907 a fence (still maintained) 1, 000 mi (1, 610 km) long was built from the north coast to the south to prevent the rabbits from invading Western Australia.

People
Most Australians are of British and Irish ancestry and the majority of the country lives in urban areas. The population has more than doubled since the end of World War II, spurred by an ambitious postwar immigration program. In the postwar years, immigration from Greece, Turkey, Italy, and other countries began to increase Australia's cultural diversity. When Australia officially ended (1973) discriminatory policies dating to the 19th cent. that were designed to prevent immigration by nonwhites, substantial Asian immigration followed. By 1988 about 40% of immigration to Australia was from Asia, and by 2005 Asians constituted 7% of the population. Also by 2005 roughly one fourth of all Australians had been born outside the country.
WR Thomas, A South Australian Corroboree, 1864, Aboriginal Australians developed the animist religion of the Dreamtime
The indigenous population, the Australian aborigines, estimated to number as little as 300, 000 and as many as 800, 000at the time of the Europeans' arrival, was numbered at 366, 429 in 2001. Although still more rural than the general population, the aboriginal population has become more urbanized, with some two thirds living in cities. New South Wales and Queensland account for just over half of the Australian aboriginal population. In Tasmania the aboriginal population was virtually wiped out in the 19th cent.

St Mary's Catholic Cathedral, Sydney,
About a quarter of Australians are Roman Catholic
There is no state religion in Australia. The largest religions are the Roman Catholic, Anglican, and other Christian groups.