
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
V free reading
|
|
Read the following passage in your own time. If there are any words you don’t know, look them up in your dictionary. Try to find additional examples of the points you have studied in this and other units.
THE WANKEL ENGINE
The Wankel engine is a form of heat engine which has a rotary piston. In other words, instead of going up and down the Wankel piston rotates in the cylinder. Both cylinder and quite different in shape from those of conventional engines. The Wanke piston is triangular with curved sides and the cylinder is roughly oval in shape. The piston has an inner bore which is linked through an eccentric gear to the output shaft. The other end of the bore is toothed and engages with a stationary gear fixed to the cylinder end. This arrangement ensures that piston follows an elliptical path round the cylinder so that the apexes of the piston, which carry gas-tight seals, are always in contact with the inside surface of the cylinder.
The piston thus forms three crescent-shaped spaces between itself and the cylinder wall, which vary in size as the piston rotates. Fuel enters the cylinder through the inlet port when one of these spaces is increasing in size. The fuel trapped in this section is then compressed by the turning piston and ignited by the sparking plug.
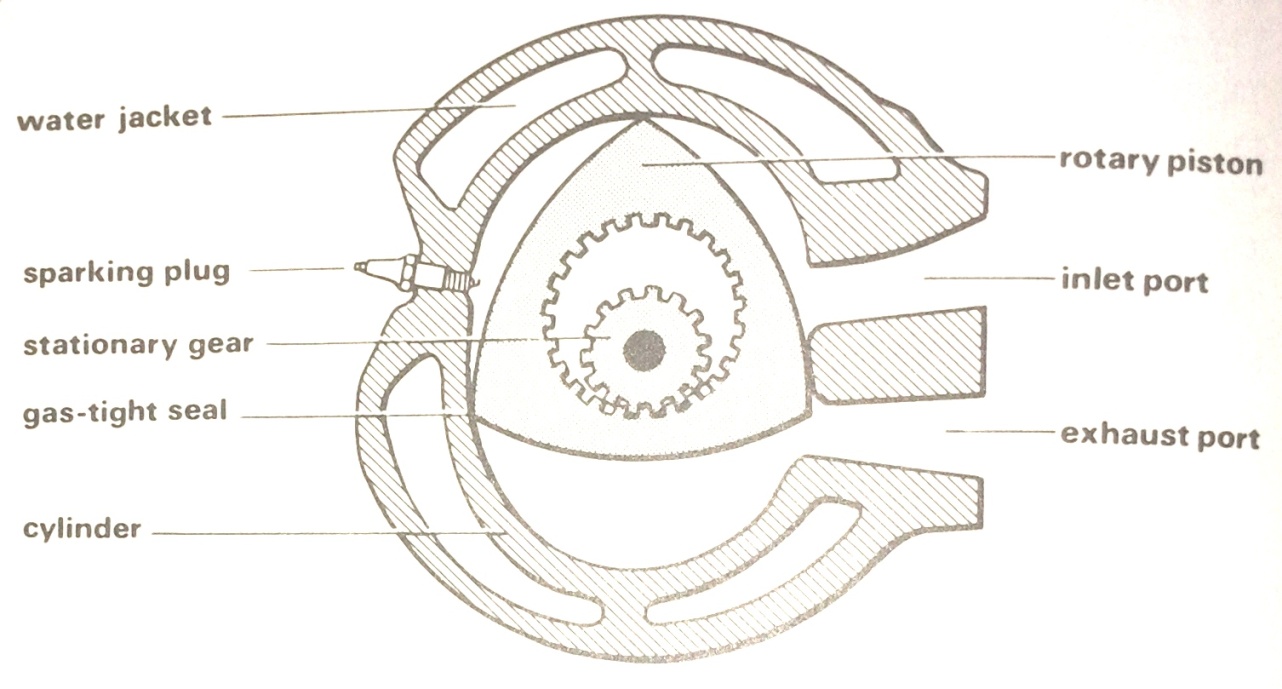
The expanding gases subject the piston to a twisting moment which makes the piston revolve further until the exhaust gases escape through the exhaust port. A fresh charge is then induced into the cylinder. Meanwhile the same process is being repeated in the other two spaces between the piston and the cylinder.
The Wankel engine has many advantages over the reciprocating piston engine. Fewer moving parts are necessary because it produces a rotary movement without using a connecting rot and a crankshaft. Because of this rotary movement it has no vibration. In addition it has no valves, it is smaller and lighter than conventional engines of the same power, and it runs economically on diesel and several other fuels.