
√лавна€ страница —лучайна€ страница
ј“≈√ќ–»»:
јвтомобилијстрономи€Ѕиологи€√еографи€ƒом и садƒругие €зыкиƒругое»нформатика»стори€ ультураЋитератураЋогикаћатематикаћедицинаћеталлурги€ћеханикаќбразованиеќхрана трудаѕедагогикаѕолитикаѕравоѕсихологи€–елиги€–иторика—оциологи€—порт—троительство“ехнолог舓уризм‘изика‘илософ舑инансы’им舄ерчениеЁкологи€ЁкономикаЁлектроника
paradigms of gt, oe & ohg verbs
|
|
| STRONG VERBS ACTIVE Present Indicative | WEAK VERBS ACTIVE Present Indicative | ||||||||
| gt | oe | ohg | gt | oe | ohg | ||||
| I, III, IV | II | I | II | III | |||||
| Sg 1 | -a | -e | -u, -o | -a, - ― | - ― | -e | -u | -ô m, -ô n | ê m, ê n |
| -is | -st | -is(t), -est | -is | -ō -s | -st | -is(t) | - ô s(t) | -ê s(t) | |
| -iþ | -ð | -it, -et | -iþ | -ō -þ | -ð | -it | -ô t | -ê t | |
| DL 1 | ō s | ― | ― | -ō s | -ō -s | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| -ats | ― | ― | -ats | -ō -t | ― | ― | ― | ― | |
| PL 1 | -am | -u/-a /mê s, -emê s, -ê m | -am | -ō -m | -e/a / mê s, -ê m | -ô mê s, - ô (ê)n | -ê mê s, -ê (ê)n | ||
| -iþ | -að | -et, -at, -ent | -iþ | -ō -þ | -að | -et, -at | -ô t | -ê t | |
| -and | -ant, -ent | -and | -ō -nd | -ent, -ant | -ô nt | -ê nt | |||
| Presen Subjunctive | Present Subjunctive | ||||||||
| sg 1 | -au | 
| -e | -au | ― | 
| -e | - ô e | ê e |
| -ais | -e | -ê s(t) | -ais | -ō -s | -e | -ê s(t) | - ô s(t) | -ê s(t) | |
| -ai | -e | -ai | ― | -e | - ô e | -ê e | |||
| DL 1 | -aiwa | ― | ― | -aiwa | -ō -wa | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| -aist | ― | ― | -aist | -ō -ts | ― | ― | ― | ― | |
| PL 1 |  -aima -aima
| -ê m, -ê n -a/-e/ -mê s | -aima |  -ō -ma -ō -ma
| -ê m, -ê n -a/-e/ -mê s | -ô m(ê s), - ô n, -ô ê m | -ê m(ê s), -ê n, -ê ê m | ||
| -aiþ | -en | -ê t, -ê nt | -aiþ | -ō -þ | -en | -ê t | -ô t, -ô ê t | -ê (ê)t | |
| -aina | -ê n | -aina | -ō -na | -ê n | -ô n, -ô ê n | -ê n, -ê ê n | |||
| MEDIOPASSIVE Present Indicative | MEDIOPASSIVE Present Indicative | ||||||||
| sg 1 | -ada | ― | ― | -ada - ō da | ― | ― | ― | ― | |
| -aza | ― | ― | -aza - ō za | ― | ― | ― | ― | ||
| -ada | ― | ― | -ada - ō da | ― | ― | ― | ― | ||
| PL | -anda | ― | ― | -anda - ō nda | ― | ― | ― | ― | |
| Present Subjunctive | Present Subjunctive | ||||||||
| sg 1 | -aidau | ― | ― | -aidau -ō dau | ― | ― | ― | ― | |
| -aizau | ― | ― | -aizau -ō zau | ― | ― | ― | ― | ||
| -aidau | ― | ― | -aidau -ō dau | ― | ― | ― | ― | ||
| PL | -aindau | ― | ― | -aindau -ō ndau | ― | ― | ― | ― |
The stem suffix of certain Gothic weak verbs belonging to the 2nd and the 3d classes merges with the vowel of the ending when they coincide.
| STRONG VERBS ACTIVE Past Indicative | WEAK VERBS ACTIVE Past Indicative | ||||||
| Gt | OE | OHG | Gt | OE | OHG | ||
| I-VT VII | |||||||
| Sg 1 | xТ1 -Ч | R2 Ч | xТЧ | xТ-Ч | -d-a | -d-e | -t-a |
| x 2 -t | R-(t ↓)st | xФ-e | xФ- i | -d-ē s | -d-es(t) | -t-os(t) | |
| x-Ч | R- Ч | xТ- Ч | xТ- Ч | -d-a | -d-e | -t-a | |
| DL 1 | xФ-u | R-u | Ч | Ч | -d-ē du | Ч | Ч |
| xФ-uts | R-uts | Ч | Ч | -d-ē du | Ч | Ч | |
| P1 1 | xФ-um | R-um | 
| xФ-um(ê s), -un, -en |  -d-ē dum -d-ē dum
| -t-um(ē s), -un | |
| xФ-uþ | R-uþ | xФ-on | xФ-ut, -ent | -d-ē duþ | -d-on | -t-ut | |
| xФ-un | R-un | xФ-un, -en | -d-ē dun | -t-un | |||
| Past Subjunctive | Past Subjunctive | ||||||
| Sg 1 | xФ-jau | R-jau | 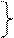
| xФ-i, -e | -d-edjau | 
| -t-i |
| xФ-eis | R-eis | -xФ-e | xФ-is, -î s(t) | -d-edeis | -d-e | Ч | |
| xФ-i | R-i | xФ-i, -e | -d-edi | -t-i | |||
| Dl 1 | xФ-eiwa | R-eiwa | Ч | Ч | -d-ē deiwa | Ч | Ч |
| xФ-eits | R-eits | Ч | Ч | -d-ē deits | Ч | Ч | |
| P1 1 | xФ-eima | R-eima | 
| xФ-î m(ê s) | -d-ē deima | 
| -t-î m(ê s) |
| xФ-eiþ | R-eiþ | xФ-en | xФ- î t, î n | -d-ē deiþ | -d-en | -t-î t | |
| xФ-eina | R-eina | xФ-î n | -d-edē ina | -t-î n | |||
| Imperative | Imperative | ||||||
| Sg2 | 3 Ч | - Ч | - Ч | -ei-o-a-n | Ч | Ч | |
| -adau | Ч | Ч | -adau4 | Ч | -i | ||
| D12 | -ats | Ч | Ч | -ats | Ч | Ч | |
| P1 1 | -am | Ч | -a/-e/mê s, -ê m, -ê n | -am | Ч | -e/-a/mê s, -o(ê)n, - ê ê n | |
| -iþ | -að | -ê t, -at, -ê nt | -iþ | -að | -et, -at, -ô t, -ê t | ||
| -andau | Ч | Ч | -andau | Ч | Ч |
1xТ denotes that the past singular stem of the strong verb is used;
xФ denotes that the past plural stem of the strong verb is used.
2R - the reduplication is used in form-building.
3The Imperative stem coincides with the Infinitive stem.
4The stem suffixes vary from the 1 to the 4th classes. A completer table should be consulted for details.
PROTO-GERMANIC VOCABULARY
TABLE 16
OLD GERMANIC VOCABULARY
| ETYMOLOGICAL CHRONOLOGICAL LAYERS | |||
| COMMON INDO-EUROPEAN LAYER | Lexical isoglosses cover all the areals of the Indo-European language community. The areal of the isoglosses can be wider, narrower, or it can cover only two or three areals, as: Germanic-Baltic lexical isoglosses Germanic-Slavonic Germanic-Baltic-Slavonic Gennanic-Celtic Gennanic-Italic Celtic-Italic-Germanic | OE «rindan, Lith gré ndu OIcel borr, OR δ оръ OIcel vax, Lith vaskas, OSlav воск OE rū m, Olr rú n OE «ræ s, L grā men OIr cnū, L nú x, OE hnutu | |
| COMMON GERMANIC LAYER | These words do not have etymological parallels in other IE languages. These isoglosses do not cross the boundaries of the Germanic language community Gothic-Scandinavian lexical isoglosses(68) West Germanic lexical isoglosses (60) | Gt fraiw, Olcel fræ, frjo 'family' OE cninht, OHG kneht 'servant' | |
| NATIONAL WORDS | Words which appeared in different Old Ger≠manic languages after their separation from the Common Germanic language community | OE clipian 'to call' OE brid 'bird' OE hlafō rd 'lord' | |
| STYLISTIC DIFFERENTIATION | |||
| NEUTRAL VOCABULARY | Commonly used words denoting productive activity of men, elementary notions and things | ||
| STYLISTICALLY COLOURED WORDS | Poetic words used in Old Germanic epic texts: metaphors, kennings, epithets, comparisons Words used in philosophical, law, religious texts - learned words Texts of runic inscriptions - stereotyped formulas, usage of specific sacred words, deliberate omission or addition of certain runes in inscriptions | OE swan-rad (way of swans) 'sea' Alu, auja, erliaR, lau, laukaR | |
| SEMANTIC DIFFERENTIATION | |||
| Depending on the lexical meaning the words fell into different semantic spheres as natural phenomena, productive activity, names of men, animals, plants, main qualities, actions, etc. | |||
OE vocabulary is believed to comprise from 30.000 to 100.000 words. Up to 70% of the Modern English vocabulary consist of the loan words, and only 30% of the words are native.
The Common IE word-stock and the Common Germanic words form the bulk of the most frequent elements used in any style of speech (no less than 80% of 50% of the most frequent words of Modem English).
TABLE 17
COMMON INDO-EUROPEAN VOCABULARY
| NOUNS Natural phenomena and environment - meteorological phenomena snow, rain, cold - physical objects hill, dale, mar- - seasons, parts of the day Names of animals, birds, plants Parts of the human body heart, ear, nose, tooth, head, foot Terms of kinship father, mother, daughter, sister Productive activity - stock-breeding, agriculture cattle, cow, sheep, milk, wool, com, barley, crops, plough -some metals and their processing copper, iron | cold: IE*gel-, Gt calds, OE ceald, OHG kalt hill: OE hyll, L Collis, Lith calnas crane: Gr geranos, L grьs, OE cran apple: OE appel, OHG apful, Lith obelis, R €блоко heart: Gt hairto, OE heorte, Gr kardia, L cor father: Gt fadar, OE fæ der, OHG fater, L pater cattle: Skr pá ç uh, L pecus, Gt faí hu, OE fē oh corn: Gt caú rn, OHG korn, OE corn, L grā num copper: Gt aí z, OE ā r, OHG ê r, L aes, OInd ayas |
| VERBS - denoting basic activities of men be, live, die, eat, sleep, hear, see, go, stand, sit, run, know - agricultural activity plough, till, sow, milk | know: Gr gignō skō, L cognō scō, Gt kunnan plough: Gr aró ō, L arō, Gt arjan milk: Gr amé lgein, L mulgeō, OE melcan, OHG melchan |
| ADJECTIVES big, new, old, young, hot, red | red: Skr rudhirá h, L ruber, U рудий, Gt rauÞ s |
| PRONOUNS Personal, interrogative... | I: Skr ahá m, L egō, OE ic who: Skr kah, L quis, Gt h as, R кто |
| NUMERALS | eight: Skr astā, Gr ó ctō, L ó ctoō, Gt ahtau hundred: Skr catá m, Gr (he)cató n, L centum, R сто, Avest satm |
| PREPOSITIONS AND CONJUNCTIONS | of: Skr à ра, Gr apó, L ab, OE of for: Skr pra-, L pro, Gt faú r, OE for, R про |
TABLE 18
COMMON GERMANIC VOCABULARY
| NOUNS The most important objects and natural phenomena - atmospheric phenomena - physical objects - seasons, time Names of animals, birds, plants Names of men and parts of a human body Names of different objects. clothes house, ship, bridge, cloth, shirt Abstract notions | frost: OE, OSax, Olcel frost, OHG vrost storm: OE storm, OHG sturm, Olcel stormr sea: Gt saiws, OE sæ, OHG sē o, OIcel sǽ r time: OIcel tið, OE tī d, OHG zî t horse: OE hor, OHG (h)ros, OIcel hross hand: OE hand, OHG hant, OIcel hend bridge: OE №rус«, OHG brucka hope: OE пора, OHG hoffe, Sw hopp |
| VERBS bake, burn, buy, drive, hear, keep, like, send, drink, hold, speak | drink: Gt drigkan, OE drincan, OHG trinkan send: Gt sandjan, OE sendan, OHG senten |
| ADJECTIVES broad, sick, own, little, high, green, blue | own: OE а«еn, OHG eigan, OIcel eiginn |
| PRONOUNS such, they, their, them, some, both | such: Gt swaleiks, OE swile, OHG solih |
| ADVERBS | often: Gt ufta, OE, OHG, OIcel oft |
| LOAN WORDS CELTIC BORROWINGS | |
| iron whisky, Exe, Esk Avon, Evan, Loch Ness London < L Londiniun < Celt Llyndū n | Celt *isarno, Oh- iarann > Gt eisarn, OE isern, iren, OHG isarn, Olcel isarn, iarn Celt usige СwaterТ, avon СriverТ, loch СlakeТ Celt dū n СhillТ |
| THE EARLIEST LAYER OF LATIN BORROWINGS | |
| Refer to material culture, trade, agriculture, cooking: port, -caster, -ehester (Lancaster, Man≠chester, Portsmouth), wall, street, mile, ketue, dish, kitchen, cup, pound, inch, butter, cheese, cherry, pear, wine, mint, pepper, mill... | port < L portus СharbourТ -caster < L castra Сcamp, fortТ wall < L vallum Сsheft, fencingТ street < L strata via Сpaved roadТ mile < Lmilliapassum Сone thousand stepsТ |