
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Fig.8 The transient processes of control systems.
|
|
This general solution has the following form:
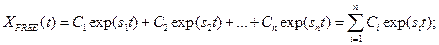 (1.23)
(1.23)
where:
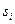 - the roots of system characteristic equation
- the roots of system characteristic equation 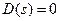 ;
;
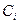 - integration constants which are defined by initial conditions.
- integration constants which are defined by initial conditions.
Thus, Eq.(1.23) describes a transient process - the system free movement.
A linear control system whose transient process represents the oscillation damping in the course of time (when the amplitude of 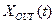 is continuously diminishing) is called a stable control system according to the following condition:
is continuously diminishing) is called a stable control system according to the following condition:
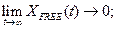 (1.24)
(1.24)
If the condition Eq.(1.24) isn’t satisfied then we obtain an unstable control system with the un-damped transient process.
B. The particular solution – the system forced movement component.
The 2nd component solution describes the system forced movement in steady-state regime.
We assume that a forced input action is a harmonic function:
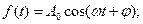 (1.25)
(1.25)
where:
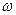 - a circular frequency of oscillation;
- a circular frequency of oscillation;
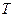 - a period of oscillation;
- a period of oscillation;
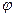 - a phase shift.
- a phase shift.
We assume that the phase shift is equal to 0, in this case the input harmonic action will be:
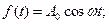 (1.26)
(1.26)