Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
FIGURE 4.8 Typical voltage response for underdamped RLC circuit.
|
|
The solution of heterogeneous (inhomogeneous) differential equation of one-dimensional control system (Eq.(1.15)) will have two components:
- the general solution of homogeneous differential equation which describes the system free movement or its transient process;
- the partial [particular] solution of heterogeneous differential equation which describes the system forced movement.
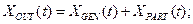 (1.22)
(1.22)
A The general solution
The integral of homogeneous differential equation
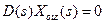 describes the system free movement which is defined by the system dynamic properties.
describes the system free movement which is defined by the system dynamic properties.
The steady-state process of a control system means its behavior after the termination of its transient process (on condition that 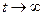 and
and 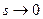 ).
).
The system free movement represents the system behavior after the moment when this system was forced to leave its equilibrium state being effected by some input action (we suppose that this input action has a limited duration).
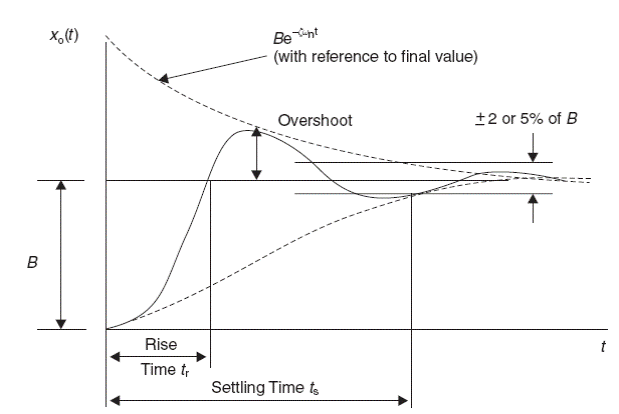
Fig.2 The transient process of the 2nd order under-damped control system
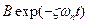
where 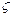 is the dimensionless damping ratio, and
is the dimensionless damping ratio, and  is the natural frequency of the
is the natural frequency of the
system.