
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
E. Quadratic and cubic input time power functions.
|
|
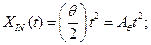 (4.45)
(4.45)
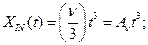 (4.46)
(4.46)
You may construct quadratic and cubic input time power functions blocks using the following blocks from Matlab6.5:
- Ramp;
- Math Function (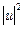 ).
).
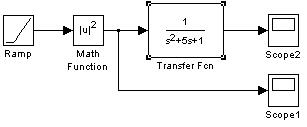
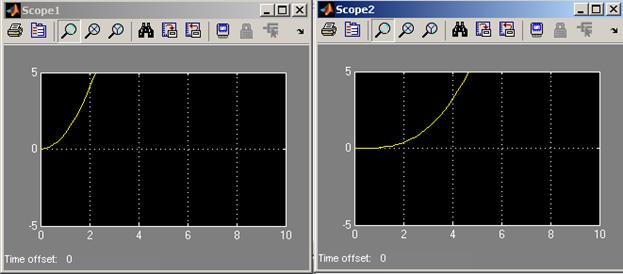
FIGURE 4.15 Block diagram, input and output signals for a 2nd order control system.
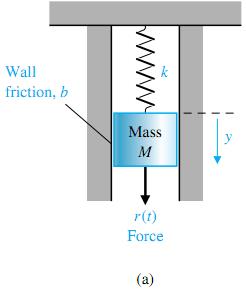
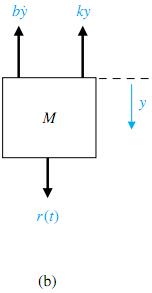
6(a) is described by Newton's second law of motion. (This system could represent, for example, an automobile shock absorber). The free-body diagram of the mass M is shown in Figure 4.6(b).
In this spring-mass-damper example, we model the wall friction as a viscous damper, that is, the friction force is linearly proportional to the velocity of the mass. In reality the friction force may be-have in a more complicated fashion. For example, the wall friction may behave as a
Coulomb damper. Coulomb friction, also known as dry friction, is a nonlinear function of the mass velocity and possesses a discontinuity around zero velocity. For a well-lubricated, sliding surface, the viscous friction is appropriate and will be used here and in subsequent spring-mass-damper examples. Summing the forces acting on M and utilizing Newton's second law yields
| 
|