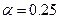Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Fig.4.5 Transient and steady-state periods of time response
|
|
The time response of any system has two components:
1. Transient response: This component of the response will (for a stable system) decay, usually exponentially, to zero as time increases. It is a function only of the system dynamics, and is independent of the input quantity.
2. Steady-state response: This is the response of the system after the transient component has decayed and is a function of both the system dynamics and the input quantity.
The total response of the system is always the sum of the transient and steady-state components. Figure 4.5 shows the transient and steady-state periods of time response. Differences between the input function 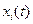 (in this case a ramp function) and system response
(in this case a ramp function) and system response  are called transient errors during the transient period, and steady-state errors during the steady-state period. One of the major objectives of control system design is to minimize these errors.
are called transient errors during the transient period, and steady-state errors during the steady-state period. One of the major objectives of control system design is to minimize these errors.
To design any control system it’s necessary to analyze its operation at various working conditions (the main problem is to measure the system reaction to many types of input actions).
To simplify testing process we must choose typical input actions (including input control signals and disturbance input signals) which are similar to real input actions (i.e. to be sure that after a testing procedure and analysis this control system will work properly under various possible working conditions).
System reaction to typical input signals will define main system properties (mostly its dynamic features).
There are several typical input signals:
- step function;
- 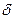 -function;
-function;
- harmonic (sine-shaped) input signal;
- ramp (linear increasing) input signal;
- quadratic (parabolic) time function and others.
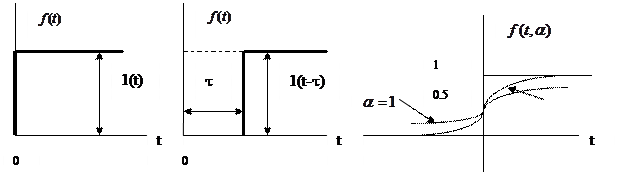
- Step function.
Step function is indicated as:
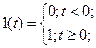 (4.28)
(4.28)
The system reaction to unit step function is called the transient characteristic, transient process (step response) or transient function 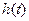 .
.
|