
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Measurement procedure and experimental equipment
|
|
In this laboratory work, the oscillatory motion of a mathematical pendulum is used to study random distribution and determine gravity acceleration.
 Mathematical (simple) pendulum is an abstraction – material point suspended on a weightless unstretchable thread. It can be represented as metal sphere (called bob) suspended on a thin thread. The diameter of the bob is much less than the length of a thread; the oscillations are performed in air medium (force of medium resistance may be ignored); the angle of thread deviation about equilibrium position has a small value (3 … 5o). If such a system is off balance, it will perform free undamped harmonic oscillations.
Mathematical (simple) pendulum is an abstraction – material point suspended on a weightless unstretchable thread. It can be represented as metal sphere (called bob) suspended on a thin thread. The diameter of the bob is much less than the length of a thread; the oscillations are performed in air medium (force of medium resistance may be ignored); the angle of thread deviation about equilibrium position has a small value (3 … 5o). If such a system is off balance, it will perform free undamped harmonic oscillations.
Pendulum (Fig. 5.4), deviated on an angle a from equilibrium position, performs harmonic oscillations under the influence of restoring force F which is a resultant of gravity force P and thread tension Q.

 so
so  ,
,
where m is mass of the ball; g is gravity acceleration.
As the sine of a small angle is equal to the value of the angle, we have
 ,
,
where x is displacement of a pendulum with reference to equilibrium position; l is the length of a pendulum thread. Thus
 .
.
The restoring force is tangentially directed to the bob motion trajectory and opposite to the direction of axis x, therefore there is the minus sign. According to the second Newton's law
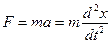 .
.
So the pendulum motion equation looks as follows:
 or
or  .
.
The angular (cyclic) natural oscillation frequency wo is defined by the system parameters
 .
.
Thus we have got a differential equation of a mathematical pendulum motion or basic equation of free undamped harmonic oscillations:
 .
.
The general solution of this equation is
 ,
,
where A is oscillation amplitude (the greatest displacement of a pendulum equilibrium position); wo t +jo is oscillation phase; jo is initial phase (oscillation phase while t = 0), wo is natural cyclic oscillation frequency (number of oscillations during 2p seconds).
A period of oscillations (time of one complete oscillation) and cyclic frequency are connected by the formula
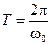 .
.
Then the period of mathematical pendulum oscillations is defined by the expression
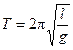 .
.
If the time of several oscillations has been measured, the period can be determined by the formula
 ,
,
where k is the number of oscillations; t is the time of oscillations.
Using the previous formulas one can get the expression for gravity acceleration magnitude determination
 . (5.7)
. (5.7)