
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Impulse buying
|
|
Impulse buying is purchases made on items a consumer had not planned on buying before leaving the house or navigating to a web page. Impulse purchases can have a hypnotic effect on a buyer due to the dopamine released in the brain when these purchases are made; the dopamine " high" is similar to using drugs or having sex. According to " Redbook" magazine, nearly half of retail and online purchases are impulsive.
Not having a list or a clear idea of what you need, can lead to impulse buying. When consumers are unsure of what to buy, they are more prone to being sucked in by attractive packaging, optimum product placement in the store or prices that seem better than they are. According to the financial website " One Mint" items presented in a shiny, attention-grabbing manner end up in a consumer's cart before a standard version of the same product. Likewise, if items are placed at eye level or at the end of an aisle, people are more likely to purchase them. They will also be more quickly drawn to items that are advertised as two for $1, rather than 50 cents, even though there is no difference in price. Grocery stores often place limits on how many sale items you can buy, another ploy to convince consumers to buy the maximum number of items even if they don't really need that many.
Consumers, in general, are influenced by characteristics of the situation, condition surrounding their shopping trip. Major situational influences include the physical surroundings, social surroundings, time, task, monetary conditions, and momentary moods.
The physical surroundings that influence buying behavior are observable features that include location of the store, merchandise display, store design, and noise level of the store. The social surroundings of a situation are other people, their characteristics and roles, and the way they interact. The moods and condition as well as the time, task, and monetary condition of a consumer time of purchase influence their buying decision. Although useful in explaining planned purchase situations, the model does not lend itself to explaining the process of impulse buying. The buying behavior is classified as planned or unplanned. According to this classification, planned buying behavior involves a time-consuming; whereas unplanned buying refers to all purchases made without such advance planning including impulse buying, which is distinguished by the relatively speedy decision-making encouraged by stimulating.
Impulse purchases are not the result of a specific search to satisfy a particular requirement. Purchases are incidental to this speedy process although they may provide some kind of enjoyment. This is are most likely happen a cause of a good mood, because when people have a good mood they want to reward yourself and buy more. It's all because of emotions.
Impulse buying research: According to the results of a recent research in hypermarket Westfield which is located in London, impulse buying accounts for 60-70% in 2012.
It is interesting to point out, that there is a tendency for women, men and children to be differently involved in impulse buying.
When we analyze women, 70% of women make unplanned shopping decision; 20% know what they want to buy, but then change their decision; 10% of women make planned shopping decision.
Looking at men, 65% of men make impulse buying; 25% know what they want, but change their decision in store; 10% know what they want and buy it.
Speaking of children (1-12 years old), 97% make impulse buying; 2% know what they want, but then change their mind, 1% buy what they planned (see Сhart 1 below).
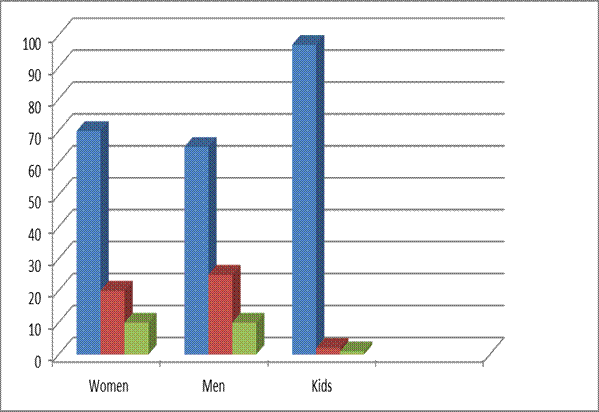
Chart 1: Impulse buying