
Главная страница Случайная страница
КАТЕГОРИИ:
АвтомобилиАстрономияБиологияГеографияДом и садДругие языкиДругоеИнформатикаИсторияКультураЛитератураЛогикаМатематикаМедицинаМеталлургияМеханикаОбразованиеОхрана трудаПедагогикаПолитикаПравоПсихологияРелигияРиторикаСоциологияСпортСтроительствоТехнологияТуризмФизикаФилософияФинансыХимияЧерчениеЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника
Example 3.
|
|
Find the particular solution of the differential equation D(D-5)y = 0 which has value equal to 2 and derivative equal to -15 when x = 0. The characteristic equation is t(t - 5) = 0, whose roots are obviously 0 and 5. The general solution is therefore
 y=c1e0x+c2e5x=c1+c2e5x
y=c1e0x+c2e5x=c1+c2e5x
The derivative is y’=5c2e5x.
When x = 0, we are told that y = 2 and y’ = -15. Substituting these values in the preceding equations, we obtain
2=c1+c2e5.0=c1+c2
-15=5c2e5.0=5c2.
It follows that c2 = -3 and thence that c1 = 5. Hence the required solution is
y=5-3e5x.
It is extremely useful to recognize alternative forms of the general solution of the differential equation (D2 + aD + b)y = 0 in the case where the roots of the characteristic equation are the complex numbers α + iβ and α - iβ. In particular, it is easy to verify that the functions
y=ceα xsin(β x+k), (1)
y=ceα xcos(β x+k) (2)
where c and k are arbitrary real numbers, are both solutions. To see that this is so, we expand (1) using the trigonometric identity for the sine of the sum of two numbers. The result is
y = ceα x(sin β x cos k + cos β x sin k)
= eα x[(c sin k) cosβ x + (c cos k) sinβ x].
Setting c1 = c sin k and c2 = c cos k, we obtain y = eα x (c1 cosβ x+c2 sinβ x), which we know to be a solution. The proof for (2) is analogous.
Conversely, any solution y = eα x (c1 cosβ x+c2 sinβ x) can be written in the forms (1) and (2). For if both c1 = c2 = 0, then y = 0, and we need only set c = 0 in (1) and (2). If c1 and c2 are not both zero, then 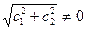 , and we can write
, and we can write
y=  eα x
eα x 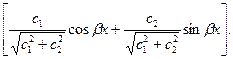
To put this equation in the form of (1), we set c =  and observe that, since
and observe that, since 
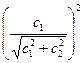 = 1
= 1
it follows from our definition of the functions sine and cosine that there exists a real number k such that cos k =  and sin k=
and sin k=  . Hence, we get
. Hence, we get
y = ceα x(sin k cos β x + cos k sin β x)
= ceα xsin (β x +k).
Again, by an analogous argument, the solution can also be written in the form of equation (2).
An advantage in using the forms (1) and (2) for the general solution is that it is easy to see what the graphs of such functions look like. They are all sinusoidal curves lying between the graphs of y = ceα x and y = - ceα x.
Give the English equivalents for: получить; производная; равный; подставить эти значения; корни характеристического уравнения; требуемое решение; доказать; доказательство; произвольные вещественные числа; наблюдать; можно записать; кривые.
Grammar Notes: